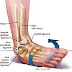
Ankle sprains are among the most common musculoskeletal injuries, affecting people of all ages and activity levels. This condition occurs when the ligaments of the ankle are stretched or torn, typically due to a sudden twist or turn. While often considered a minor injury, an ankle sprain can range in severity and significantly impact an individual’s mobility and quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of ankle sprains, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Causes of Ankle Sprains
Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments surrounding the ankle are forced beyond their normal range of motion, leading to damage. The most common causes include:
Trauma or Injury:
- Description: Direct impact or sudden movements that stress the ankle ligaments.
- Examples: Stepping awkwardly on an uneven surface, landing improperly from a jump, or twisting the ankle during sports or physical activities.
Overuse:
- Description: Repetitive stress on the ankle that weakens or strains the ligaments over time.
- Examples: Repeatedly running on hard surfaces or engaging in sports that involve frequent changes in direction.
Weak or Imbalanced Muscles:
- Description: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles around the ankle can make it more susceptible to injury.
- Examples: Poor muscle conditioning or lack of proper warm-up and stretching.
Improper Footwear:
- Description: Shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can increase the risk of an ankle sprain.
- Examples: Wearing high heels, unsupportive sneakers, or shoes that do not fit properly.
Symptoms of Ankle Sprains
The symptoms of an ankle sprain can vary depending on the severity of the injury, which is classified into three grades:
Grade I (Mild Sprain):
- Symptoms: Mild stretching or microscopic tears in the ligaments. Symptoms include slight pain, minor swelling, and minimal loss of function. The ability to bear weight is typically unaffected.
Grade II (Moderate Sprain):
- Symptoms: Partial tearing of the ligaments. Symptoms include moderate pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty bearing weight. There may be a noticeable loss of range of motion and stability.
Grade III (Severe Sprain):
- Symptoms: Complete tearing or rupture of the ligaments. Symptoms include severe pain, significant swelling, bruising, and an inability to bear weight. The ankle may feel unstable, and there may be a visible deformity or abnormal movement.
Diagnosis of Ankle Sprains
Accurate diagnosis of an ankle sprain involves several steps:
Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Description: A healthcare provider will ask about the injury mechanism, symptoms, and perform a physical examination to assess pain, swelling, tenderness, and range of motion.
Imaging Studies:
- X-rays: To rule out fractures or bony abnormalities. X-rays are often performed to ensure that the injury does not involve broken bones.
- MRI or Ultrasound: May be used to evaluate soft tissue damage, including the extent of ligament tears or damage to surrounding structures.
Treatment of Ankle Sprains
The treatment of an ankle sprain depends on the severity of the injury and aims to reduce pain, promote healing, and restore function. Common treatment approaches include:
Rest:
- Description: Limiting activity and avoiding putting weight on the injured ankle.
- Purpose: To allow the ligaments to heal and prevent further damage.
Ice:
- Description: Applying ice to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours post-injury.
- Purpose: To reduce swelling and numb the pain.
Compression:
- Description: Using an elastic bandage or compression wrap to help control swelling.
- Purpose: To provide support and reduce fluid accumulation in the injured area.
Elevation:
- Description: Keeping the injured ankle elevated above the level of the heart whenever possible.
- Purpose: To reduce swelling and promote fluid drainage.
Medication:
- Description: Over-the-counter pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Purpose: To manage pain and inflammation.
Rehabilitation:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and therapies to restore range of motion, strength, and stability. Rehabilitation helps in recovering normal function and preventing future injuries.
- Balance and Strengthening Exercises: Include activities that improve ankle strength, flexibility, and proprioception (awareness of the ankle’s position).
Supportive Devices:
- Braces or Ankle Supports: To provide additional stability and protect the ankle during the healing process.
- Purpose: To prevent reinjury and support the healing ligaments.
Surgery:
- Description: Required in severe cases where there is complete ligament rupture or significant instability.
- Purpose: To repair torn ligaments and restore ankle stability.
Prevention of Ankle Sprains
Preventing ankle sprains involves taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of injury:
Strengthening Exercises:
- Description: Regular exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve stability.
- Examples: Ankle dorsiflexion, calf raises, and balance exercises.
Proper Footwear:
- Description: Wearing supportive shoes that provide proper cushioning and stability.
- Examples: Athletic shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
Warm-Up and Stretching:
- Description: Properly warming up and stretching before physical activities.
- Purpose: To prepare the muscles and ligaments for activity and reduce the risk of strains and sprains.
Avoiding High-Risk Activities:
- Description: Being cautious during activities that pose a high risk of ankle injuries.
- Examples: Using proper techniques and protective gear during sports or uneven terrain.
Conclusion
Ankle sprains are common injuries that can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for managing the injury effectively and promoting a swift recovery. Proper rest, ice, compression, elevation, and rehabilitation play vital roles in the healing process. Preventive measures, such as strengthening exercises and appropriate footwear, can help reduce the risk of future sprains. By addressing ankle sprains with timely and appropriate care, individuals can return to their normal activities and maintain optimal ankle health.
 Reviewed by Dr Naveed
on
August 03, 2024
Rating:
Reviewed by Dr Naveed
on
August 03, 2024
Rating:






No comments: